Major stem cell discovery to boost research into development and regenerative medicine
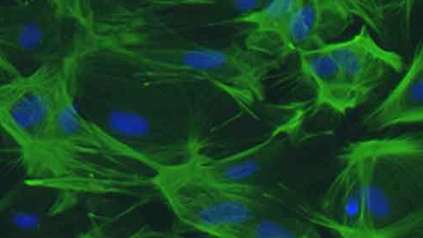
A new approach has enabled researchers to create Expanded Potential Stem Cells (EPSCs) of both pig and human cells. These stem cells have the features of the very first cells in the developing embryo, and can develop into any type of cell. The research from LKS Faculty of Medicine of The University of Hong Kong (HKUMed), the Wellcome Sanger Institute, and the Friedrich-Loeffler-Institut in Germany offers incredible potential for studying human development and regenerative medicine.
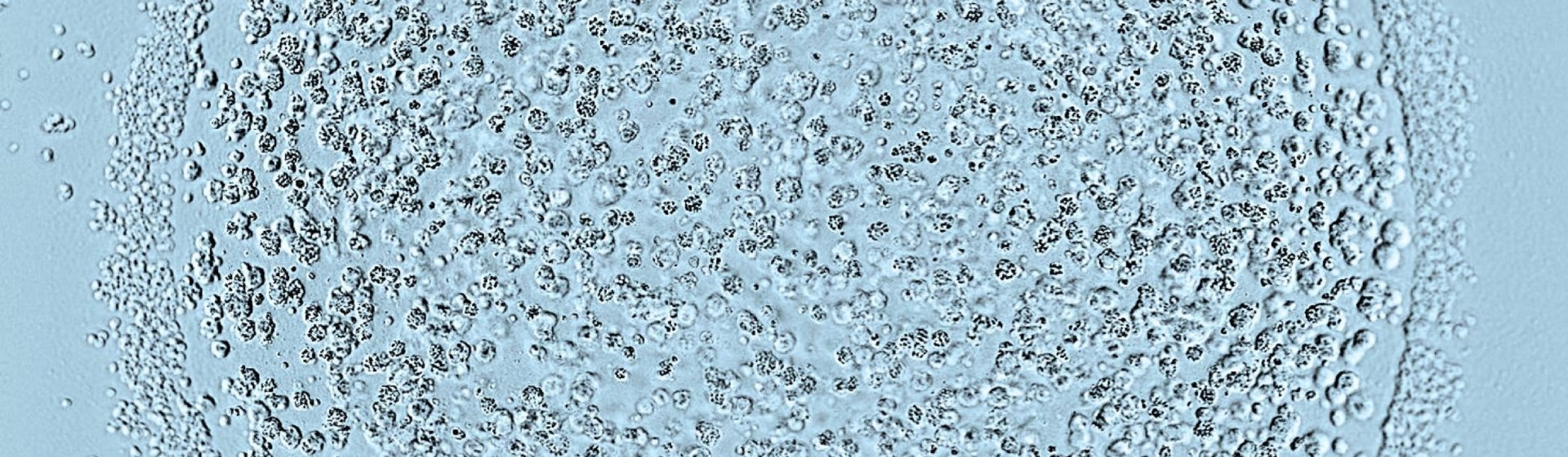
The study published in Nature Cell Biology today (3rd June) is the first time scientists have been able to derive stem cells from early pig embryos. Domestic pigs have great potential for biomedical research because of their genetic and anatomical similarities to humans, including comparable organ sizes. Being able to genetically-modify pig stem cells will also be beneficial for animal health and food production.
Stem cells have the ability to develop into other cell types, and existing stem cell lines are already extremely useful for research into development, disease and treatments. However, currently available types of stem cell lines have limitations, and until now it has also not been possible to create embryonic stem cells from pigs and many other farm animals.
“Scientists have been attempting to derive porcine embryonic stem cells for decades without much success. With our Expanded Potential Stem Cell technology, we have now successfully derived and characterised stem cells from porcine preimplantation embryos. We have also established similar human stem cells. Our study represents a significant advance in stem cell research.”
Professor Pentao Liu The leader of the study from the School of Biomedical Sciences and Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine Consortium, HKUMed, and previously of the Wellcome Sanger Institute
Since human EPSCs can produce large numbers of placenta cells – called trophoblasts – they offer new opportunities to investigate pregnancy complications such as pre-eclampsia and miscarriages.
EPSCs come from culturing cells from the earliest stage of development, when the fertilised egg has only divided into 4 or 8 cells and the cells retain some totipotency – the ability to produce all cell types.
“These EPSC stem cells possess developmental potency that is not generally seen in conventional embryonic or induced pluripotent stem cells. They have the potential to produce all embryonic and extra-embryonic cell lines – including those in the placenta and yolk sac, turning back the development clock to the very earliest cell type. These cells will enable researchers to study early embryonic development, miscarriage and developmental disorders.”
Dr Xuefui Gao A first author on the paper from HKUMed, and previously from the Wellcome Sanger Institute
The first EPSCs were created in 2017, when the group targeted key molecular pathways during very early development in mice. At these very earliest embryonic developmental stages, mammalian species are very similar and the cells are like a blank sheet of paper. This study has shown that it is possible to use the same approach to create human EPSCs and also to establish EPSCs from pigs – mammals that had previously been elusive to stem cell researchers.
“Our porcine EPSCs isolated from pig embryos are the first well-characterized pig cell lines worldwide. EPSC’s great potential to develop into any type of cell provides important implications for developmental biology, regenerative medicine, organ transplantation, disease modelling, and screening for drugs.”
Dr Monika Nowak-Imialek An author on the paper from the Friedrich-Loeffler-Institut (FLI) in Germany
More information
Publication:
Xuefei Gao, Monika Nowak-Imialek, Xi Chen et al. (2019) Establishment of porcine and human expanded potential stem cells. Nature Cell Biology. DOI: 10.1038/s41556-019-0333-2
Funding:
This work was supported by Wellcome, HKUMed and HKU internal funding and other funders. Please see the paper for full funding details.
Selected websites
About LKS Faculty of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong (HKUMed)
The LKS Faculty of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong (HKUMed) is the longest established institution of higher education in Hong Kong. It was founded as the Hong Kong College of Medicine for Chinese by the London Missionary Society in 1887, and was renamed the Hong Kong College of Medicine in 1907.
The Medical Faculty was deemed as the premier Faculty when the University of Hong Kong was established in 1911. Serving Hong Kong for over a century, it has firmly established itself as a medical school of learning, innovation, and enterprising; it is a medical school of moral, vision, and care. Ever since its inception, the Faculty has been playing a pioneering role in medical education, training and research.
From its modest beginnings, the Medical Faculty has now become the largest faculty of the University, with over 400 full-time academic and academic-related staff and over 800 research and research-related support personnel. The undergraduate student population is about 2,900 and the postgraduate student population is about 1,500. The Faculty is comprised of 14 departments, School of Biomedical Sciences, School of Chinese Medicine, School of Nursing, School of Public Health, as well as a number of research centres focusing on various strengths of research.
Friedrich-Loeffler-Institut in Germany
As Federal Research Institute for Animal Health, the Friedrich-Loeffler-Institut (FLI) addresses farm animal health and welfare. The work aims at the prevention, diagnostics and control of animal diseases, the improvement of animal welfare and animal nutrition as well as the preservation and use of farm animal genetic resources. https://www.fli.de/en/home/
Wellcome Sanger Institute
The Sanger is one of the world’s leading genome and biodata institutes. Through its ability to conduct research at scale, it is able to engage in bold and long-term exploratory projects that are designed to influence and empower science globally. Institute research findings, generated through its own research programmes and through its leading role in international consortia, are being used to develop new diagnostics and treatments for human disease and to understand life on Earth. Find out more at www.sanger.ac.uk or follow @sangerinstitute on Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn and on our Blog
About Wellcome
Wellcome exists to improve health by helping great ideas to thrive. We support researchers, we take on big health challenges, we campaign for better science, and we help everyone get involved with science and health research. We are a politically and financially independent foundation.