Sanger Institute spinout Kymab announces therapeutic antibody discovery technology
Scientists at Kymab have engineered a mouse with the full set of genes encoding the human antibody repertoire, calling this new technology Kymouse™. They have demonstrated that these mice develop an enormous range of human antibodies which can be developed as potent drugs to treat a variety of human diseases such as cancer, autoimmune and infectious diseases.
“This is a remarkable achievement in our journey towards delivering therapeutic antibodies and to facilitate vaccine development. Kymab scientists have completed the most ambitious humanisation project of the mouse genome ever undertaken, with 5.4 million bases of human DNA, representing 0.1% of the human genome into the appropriate place in the mouse genome.”
Professor Allan Bradley Founder and Chief Scientific Officer of Kymab
Antibodies are one of the best-selling classes of drugs today; five of the top ten best-selling drugs are antibodies. This is because antibodies are natural products with exquisite specificity and potency, and generally have superior safety profiles. The challenge has been to capture the full human antibody repertoire and to recapitulate all its attributes.
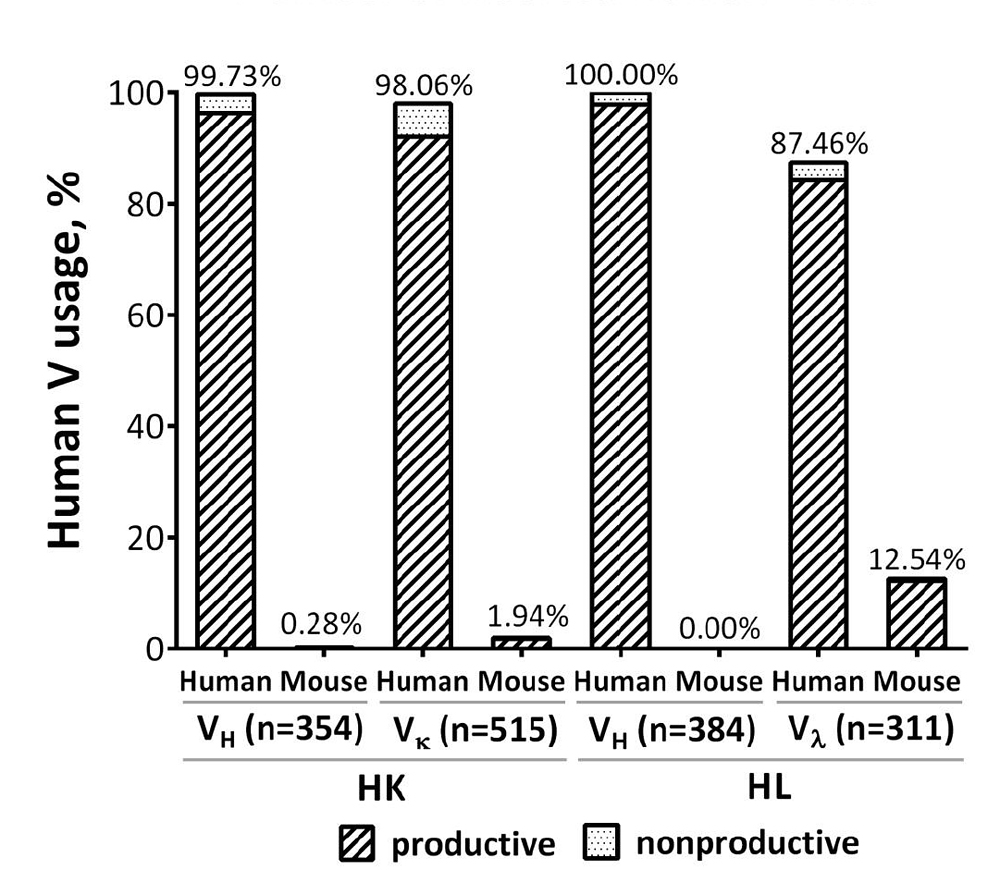
Mice with portions of the human antibody repertoire have been developed previously. However, the technology used at the time proved unsuitable for moving the very large stretches of DNA from the human genome into the mouse. As a result, their antibody gene repertoires were both incomplete and in the wrong location in the genome. Kymab scientists took a different approach and moved these vast stretches of DNA into the mouse genome in a series of steps each with a smaller segment of DNA, carefully re-joining them and thereby re-constructing the complete human repertoire in the correct place in the mouse genome.
“We are delighted to publish our technology in this highly prestigious journal and to present the first professional peer-reviewed publication of transgenic mice with a fully human antibody repertoire. Antibodies discovered using Kymouse™ strains are essentially ready to be developed as drugs. We are building a rich pipeline of first-in-class therapeutics in five areas: haematology, oncology, auto-immunity, pain and cardiovascular disease. This technology offers great potential to advance patient care in diseases with significant unmet medical need.”
Dr Christian Grøndahl Chief Executive Officer of Kymab
By using the Kymouse™ technology, Kymab can pursue the targeting of the most challenging drug targets ranging from complicated ion channels and GPCRs to deeply hidden epitopes in heavily glycosylated virus proteins.
“Kymab’s highly innovative and technically advanced Kymouse™ platform has overcome the problems which limited previous generations of human antibody generating mice and is a strong foundation on which we can build a global biotechnology company.”
Dr David Chiswell Former CEO of Cambridge Antibody Technology and Chairman of Kymab’s Board of Directors
To make these sophisticated resources widely available, Kymab has created Kymab Access, a programme that enables academic researchers to pursue the discovery and development of novel human monoclonal antibody therapeutics by partnering with Kymab and its world leading Kymouse™ antibody technology.
More information
Kymab, Kymouse, Kymouse Access are trademarks of Kymab Limited.
Publications:
Selected websites
Kymab
Kymab is a biopharmaceutical company focused on the discovery and development of fully human monoclonal antibody drugs using its proprietary Kymouse™ transgenic antibody platform.
Kymouse™ has been designed to maximise the diversity of human antibodies produced in response to immunisation with antigens. Selecting from a broad diversity of fully human antibodies assures the highest probability of finding that rare drug candidate with best-in-class characteristics. Kymab is using the platform for its internal drug discovery programmes and in partnership with pharmaceutical companies. The first Kymouse™ antibody discovery agreement was concluded with Novo Nordisk in 2013.
Founded in 2009, Kymab raised £20m of equity financing in 2010 from the investment division of the Wellcome Trust. It has an experienced management team with a successful track record in drug discovery and development and has seven current therapeutic antibody discovery programmes in immune-oncology, auto-immunity, haematology, chronic pain and cardiovascular diseases.
Kymab Access
Kymab is committed, with the support of its primary investor, The Wellcome Trust, to collaborate with leading academic experts. Kymab Access is a programme that enables academic researchers to pursue the discovery and development of novel human monoclonal antibody therapeutics by partnering researchers with Kymab and its world leading Kymouse™ antibody technology. Kymab Access is administered by Kymab Access Limited, which is a wholly owned subsidiary of Kymab established solely for this purpose with a confidentiality firewall between its operations and those of Kymab.
The Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
The Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute is one of the world’s leading genome centres. Through its ability to conduct research at scale, it is able to engage in bold and long-term exploratory projects that are designed to influence and empower medical science globally. Institute research findings, generated through its own research programmes and through its leading role in international consortia, are being used to develop new diagnostics and treatments for human disease.
The Wellcome Trust
The Wellcome Trust is a global charitable foundation dedicated to achieving extraordinary improvements in human and animal health. We support the brightest minds in biomedical research and the medical humanities. Our breadth of support includes public engagement, education and the application of research to improve health. We are independent of both political and commercial interests.