Alex Bateman takes on protein sequence services at the European Bioinformatics Institute

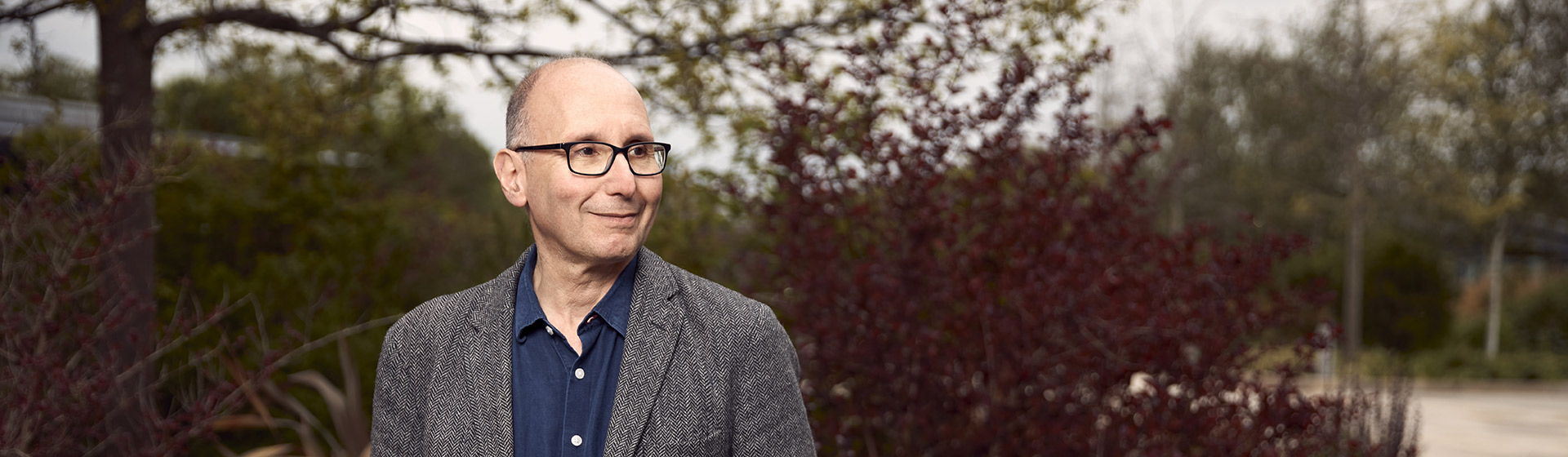
One of the UK’s leading computational biologists is stepping into a new role on the Genome Campus in Hinxton, UK. On 1 November, the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute’s Alex Bateman becomes Head of Protein Sequence Resources at the EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI).
Dr Bateman leads several projects that aim to provide a ‘periodic table’ for biology’s key molecules. During his 15 years at the Sanger Institute, he has led the development of protein and RNA family databases that are popular with researchers throughout the world: there have been around three-quarters of a million visits to Pfam and Rfam in the past 12 months alone.
“I am delighted to be moving to EMBL-EBI to work with the excellent UniProt and InterPro teams. UniProt is the most important biological database, and I am very proud to be able to help guide its future development. In addition, I believe that, as the leading centre for molecular biology resources, EMBL-EBI is a natural home for Pfam.”
Dr Alex Bateman
The Bateman group’s databases Pfam, Rfam, TreeFam and MEROPS will join EMBL-EBI’s suite of protein and proteomics resources, which includes UniProt and InterPro. UniProt is developed in close collaboration with the SIB Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics and PIR.
“Alex will come to EMBL-EBI with an enviable record in scientific research and the provision of data resources for protein and RNA sequence families. Protein services are a core component of the data services we offer from EBI and we are delighted that Alex has accepted the role to lead this part of EBI.
“Alex will take over from Rolf Apweiler, who has built up and led this group so successfully over the past 15 years. I am confident that under Alex’s leadership, together with all those involved in this work at EMBL-EBI, these resources will continue to flourish and grow to cope with an ever-changing scientific environment.”
Professor Dame Janet Thornton of EMBL-EBI
“In his research, Alex has made an enormous contribution to this Institute, and to our understanding of genomes, of RNA and of proteins. The impact of his research is reflected in the extraordinary number of citations and the recognition he has received from his peers.
“Alex has also taken a major leadership role for the Institute in the highly successful shaping of our graduate student programme, which has benefited greatly from his characteristically sensitive, thoughtful and caring approach. He has contributed beyond his science and we are extremely sorry to lose him.”
Professor Mike Stratton Director of the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
In his work at the Sanger institute, Dr Bateman has become one of the UK’s most cited researchers. He has published more than 120 scientific papers and reviews and his work has been cited almost 26 000 times by other scientists. Eight of his papers have been cited more than 1000 times. Dr Bateman was winner of the prestigious Benjamin Franklin Award for Open Data in the Life Sciences in 2010. He has been the Executive Editor for the journal Bioinformatics since 2004 and is on the Editorial Board of Nucleic Acids Research.
More information
Selected websites
Dr Bateman has led the development of the following databases, which will join EMBL-EBI’s suite of protein resources
EMBL-EBI protein resources include
Selected websites
EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI)
The EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI) is part of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and is located on the Wellcome Trust Genome Campus in Hinxton near Cambridge, UK. The EBI grew out of EMBL’s pioneering work in providing public biological databases to the research community. It hosts some of the world’s most important collections of biological data, including DNA sequences (ENA), protein sequences (UniProt), the genomes of animals and plants, three-dimensional molecular structures, data from gene expression experiments, protein-protein interactions and reactions and pathways. EMBl-EBI’s many research groups are continually developing new tools to support the biocomputing community. EMBL-EBI provides essential compute infrastructure for the ENCODE project and coordinates ELIXIR, the emerging research infrastructure for life science data in Europe.
The Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
The Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute is one of the world’s leading genome centres. Through its ability to conduct research at scale, it is able to engage in bold and long-term exploratory projects that are designed to influence and empower medical science globally. Institute research findings, generated through its own research programmes and through its leading role in international consortia, are being used to develop new diagnostics and treatments for human disease.
The Wellcome Trust
The Wellcome Trust is a global charitable foundation dedicated to achieving extraordinary improvements in human and animal health. We support the brightest minds in biomedical research and the medical humanities. Our breadth of support includes public engagement, education and the application of research to improve health. We are independent of both political and commercial interests.